What makes a rhythm complex? The influence of musical training and accent type on beat perception
Introduction
When listening to music, we often tap our feet to the beat. We infer and perceive a regular beat based on accents in the music. Accents are expected to occur on the beat, so when they are missing, the beat is more difficult to find.
When perceiving the beat pattern of a rhythm, different types of accents can be more helpful than others. The researchers tested two types of accents:
• Intensity accents are accents made by a sound that is louder than the rest of the rhythm (hereafter: intensity rhythms).
• Temporal accents are made by the grouping of time intervals in a rhythm (hereafter: temporal accents).
When perceiving the beat pattern of a rhythm, different types of accents can be more helpful than others. The researchers tested two types of accents:
• Intensity accents are accents made by a sound that is louder than the rest of the rhythm (hereafter: intensity rhythms).
• Temporal accents are made by the grouping of time intervals in a rhythm (hereafter: temporal accents).
Hypotheses
The researchers had 2 main questions.
1. Can previous musical training influence how someone perceives beats?
2. Which type of accent has a greater influence on beat perception?
1. Can previous musical training influence how someone perceives beats?
2. Which type of accent has a greater influence on beat perception?
Experiment
Participants had different musical backgrounds. Musical novices had less than 2 years of musical training. Musical experts had more than 2 years of musical training.
Participants listened to 296 rhythms and rated the difficulty of tapping along with the rhythm’s beat on a scale of 1-10.
This is an example of a temporal rhythm.
This is an example of an intensity rhythm.
Participants listened to 296 rhythms and rated the difficulty of tapping along with the rhythm’s beat on a scale of 1-10.
This is an example of a temporal rhythm.
This is an example of an intensity rhythm.
Results
|
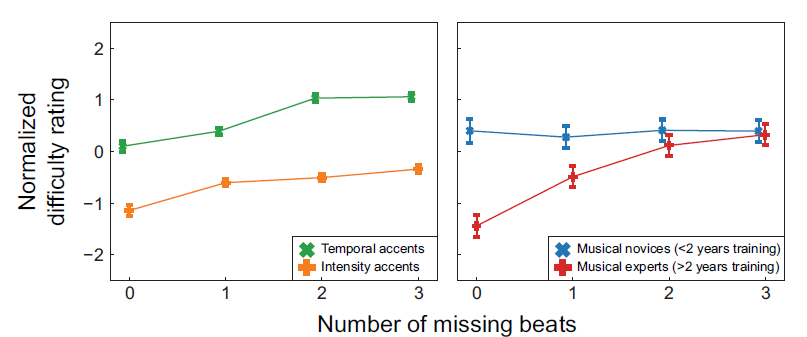
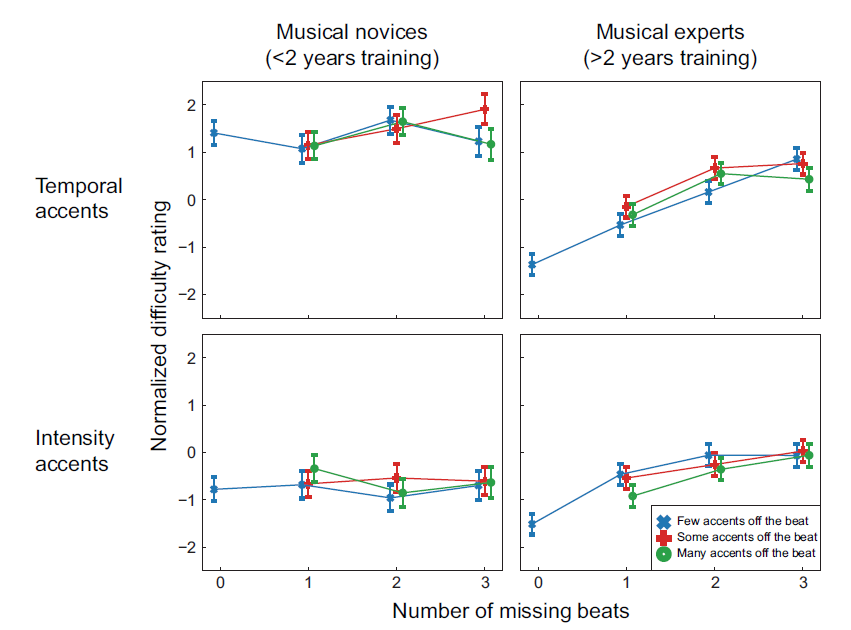
Fig 1. Negative numbers on the normalized difficulty rating indicate beats that were “easier to tap to” and positive numbers represent “more difficult to tap to”. Error bars indicate 2 standard errors. • On average, intensity rhythms were rated as “easier to tap to” than temporal rhythms, even with more missing beats. • Overall, participants with more musical training rated rhythms as “easier to tap to” than participants with less musical training Fig 2. Negative numbers on the normalized difficulty rating indicate beats that were “easier to tap to” and positive numbers represent “more difficult to tap to”. Error bars indicate 2 standard errors. • In general, rhythms with more missing beats were rated as more difficult. • For musical novices, intensity rhythms were rated as easier than temporal rhythms. • For musical experts, intensity and temporal rhythms were rated equally as easy. • Musical experts rated rhythms with temporal accents to be easier than the musical novices. • Both groups found tapping to rhythms with intensity accents equally difficult. |
Discussion and Conclusion
Overall, the findings suggest that not all listeners treat all rhythms the same.
1. Can previous musical training influence how someone perceives beats?
Yes. Participants with musical training rated rhythms as easier to tap to than musical novices. Accents on the beat facilitated beat detection in musical experts whereas musical novices didn’t appear to be affected at all. Musical experts could have developed increased sensitivity to the number of accents on the beat, allowing them to infer the beat and metrical structure. Musical experts could also have more exposure and training in listening to music.
2. Which type of accent has a greater influence on beat perception?
Temporal accents influence beat perception more than intensity accents. Participants found intensity rhythms to be easier to tap to than temporal rhythms.
1. Can previous musical training influence how someone perceives beats?
Yes. Participants with musical training rated rhythms as easier to tap to than musical novices. Accents on the beat facilitated beat detection in musical experts whereas musical novices didn’t appear to be affected at all. Musical experts could have developed increased sensitivity to the number of accents on the beat, allowing them to infer the beat and metrical structure. Musical experts could also have more exposure and training in listening to music.
2. Which type of accent has a greater influence on beat perception?
Temporal accents influence beat perception more than intensity accents. Participants found intensity rhythms to be easier to tap to than temporal rhythms.
Future Directions
Because each person can interpret accents differently, a better understanding of beat perception processes of different populations will allow clinicians to design more targeted and effective rehabilitation strategies using musical rhythm. This experiment establishes a foundation for online experiments studying beat perception.